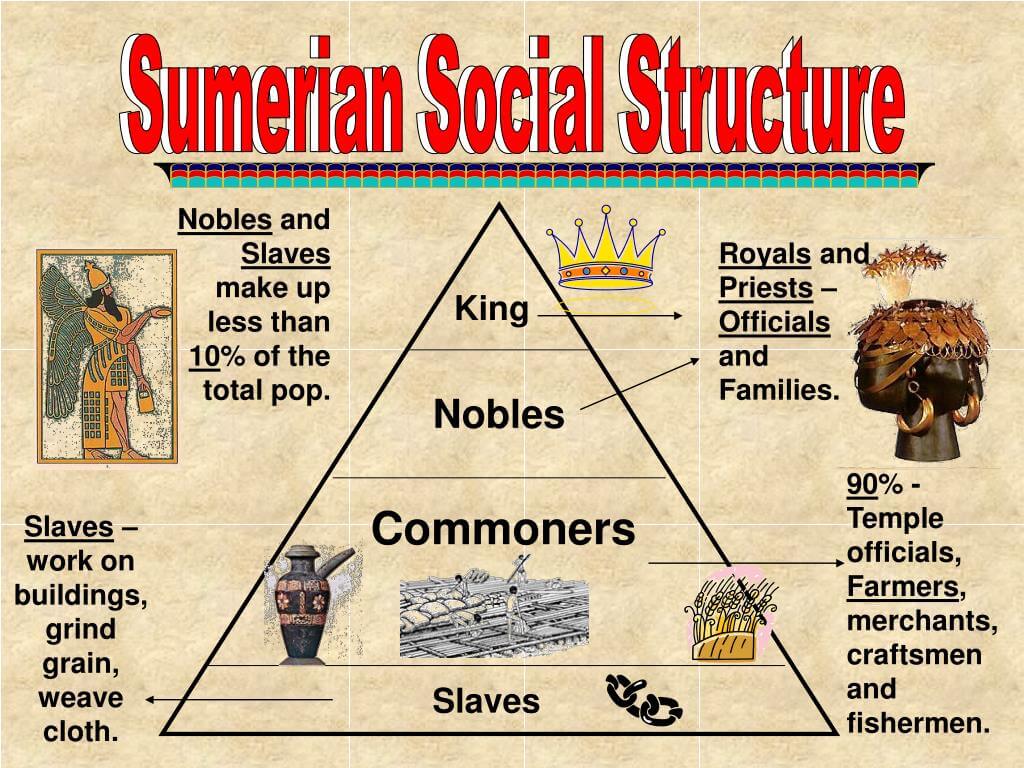
The Sumerian social structure was a complex hierarchy that defined the relationships and roles within the ancient civilization of Sumer, located in present-day Iraq. This intriguing society, known for its remarkable contributions to writing, agriculture, and urbanization, established a social system that greatly influenced its political and economic dynamics. The Sumerians created an elaborate framework that categorized individuals based on wealth, occupation, and social status, which played a crucial role in maintaining order and stability in their city-states.
In the heart of Sumer, the social hierarchy was not just a mere reflection of wealth or power; it was tightly interwoven with religious beliefs and cultural practices. The Sumerians believed that their gods favored certain individuals, granting them higher social positions, while others were seen as less favored. This belief system further solidified the stratified social classes, making it essential for individuals to understand their place within this structure. The Sumerian social structure was dynamic, with opportunities for individuals to rise or fall based on various factors, including military achievements or economic success.
The examination of the Sumerian social structure reveals not only the organization of their society but also highlights the roles and responsibilities of various classes. From the ruling elite to the laborers, each group contributed to the functioning of Sumerian society. Understanding this intricate social framework provides valuable insights into how the Sumerians navigated their daily lives, interacted with one another, and ultimately established one of the world's first civilizations.
What Were the Key Classes in the Sumerian Social Structure?
The Sumerian social structure comprised several distinct classes, each with its own characteristics and roles. The key classes included:
- Royalty and Nobility: This class included kings, priests, and high-ranking officials who held significant power and wealth.
- Priests: Serving as intermediaries between the gods and the people, priests played a crucial role in religious ceremonies and governance.
- Merchants and Artisans: This class was responsible for trade and craftsmanship, contributing to the economy's growth.
- Farmers and Laborers: The backbone of Sumerian society, this class worked the land and performed manual labor.
- Slaves: Often captured during wars or in debt, slaves had no rights and served the upper classes.
How Did Religion Influence the Sumerian Social Structure?
Religion played a pivotal role in shaping the Sumerian social structure. The Sumerians believed in a pantheon of gods, each governing different aspects of life. This belief translated into a social hierarchy where priests and religious leaders held significant power. The connection between religion and governance was evident, as kings often claimed divine right, establishing their authority based on religious legitimacy.
What Role Did Women Play in Sumerian Society?
Women in Sumerian society experienced varying degrees of freedom and responsibility depending on their social class. While upper-class women often engaged in religious activities and could own property, lower-class women typically worked alongside their husbands in agriculture or crafts. Despite the patriarchal nature of Sumerian society, some women were able to achieve a degree of influence and respect, particularly in religious contexts.
What Were the Responsibilities of Each Social Class?
Each social class in the Sumerian social structure had specific responsibilities that contributed to the overall functioning of society. The following outlines the primary duties:
- Royalty and Nobility: Governed city-states, made laws, and led military campaigns.
- Priests: Conducted religious ceremonies, maintained temples, and advised rulers.
- Merchants and Artisans: Produced goods, traded locally and internationally, and contributed to economic growth.
- Farmers and Laborers: Cultivated crops, raised livestock, and provided essential labor.
- Slaves: Performed menial tasks and served their owners without any rights.
How Did the Sumerian Social Structure Contribute to Their Success?
The Sumerian social structure was integral to the civilization's success. By clearly defining roles and responsibilities, it fostered cooperation and efficiency. The ruling class established laws and governance, while the religious class ensured social cohesion through shared beliefs. This organization allowed Sumer to innovate in agriculture, trade, and urban planning, ultimately leading to their prominence in ancient history.
What Are the Modern Implications of Studying the Sumerian Social Structure?
Understanding the Sumerian social structure has modern implications for comprehending social hierarchies in contemporary societies. The lessons learned from Sumer can inform current discussions on class, power dynamics, and the role of religion in governance. By examining the successes and failures of Sumerian society, modern civilizations can gain insights into building more equitable and harmonious communities.
The Sumerian social structure remains a fascinating subject of study, shedding light on the complexities of one of the earliest civilizations known to humankind. Its influence on subsequent societies and the lessons it offers continue to resonate, making it a vital area of research for historians and social scientists alike.
You Might Also Like
Finding Comfort: The Best Underwear For Post Vasectomy RecoveryExperience Unmatched Comfort: Discovering Qatar Premium Economy
Discovering The Age Of Rizzler: An In-Depth Look
Unveiling The Life And Age Of Actor Mark McClafferty
Exploring The Allure Of Pedro Pascal's Feet
Article Recommendations
- All Treasure Map Pieces In Another Crabs Treasure
- W Coin Listing Date And Price
- Diddy Dick Pic
- Laurie Farinacci
- Milan Cheek
- Grace Charis Net Worth
- Xxxtentacion Son
- Leslie Landon
- Cityscopenews6_0.xml
- Laura Govan Dating History