The Sumer civilization, one of the earliest known societies in human history, emerged in the southern part of Mesopotamia around 4500 BCE. This ancient civilization is renowned for its remarkable contributions to writing, architecture, and urban planning. However, one of the most fascinating aspects of Sumer is its intricate social structure, which played a critical role in shaping the daily lives of its inhabitants. By examining the Sumer social structure, we can gain a deeper understanding of how this early civilization functioned and thrived, ultimately influencing many future societies.
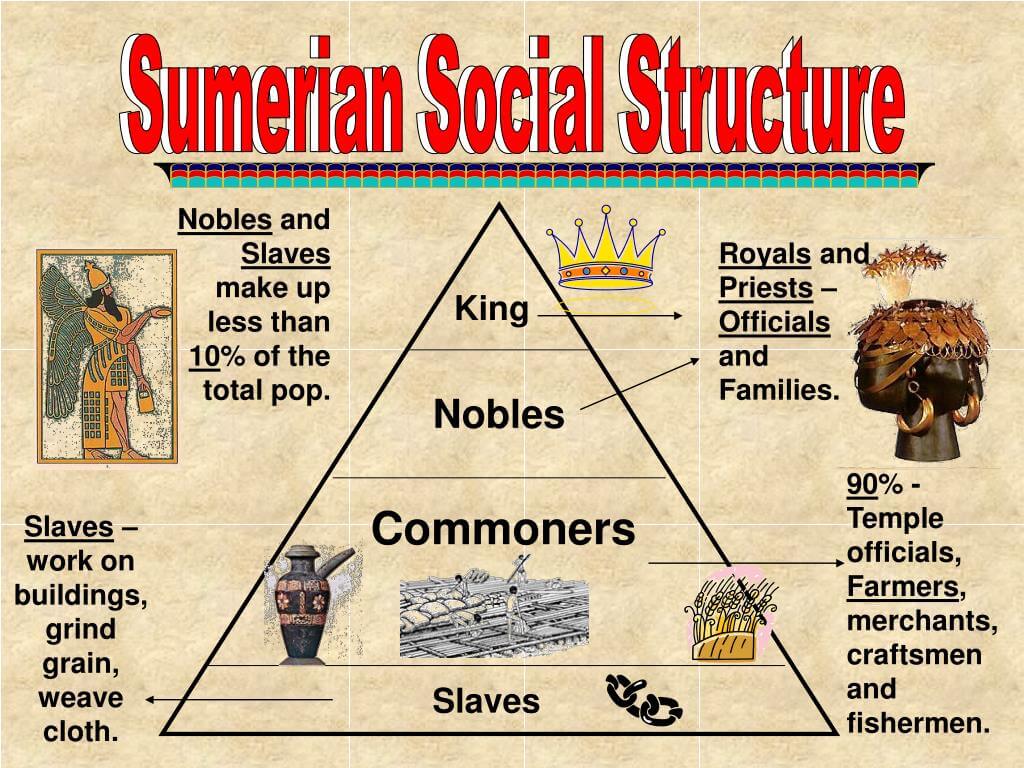
The Sumer social structure was highly stratified, consisting of various classes that defined individuals' roles, rights, and responsibilities within the community. At the top of the hierarchy were the ruling elites and priests, who wielded significant power and influence over both religious and governmental affairs. Below them were the skilled workers, artisans, and merchants, essential for the economy's functioning. At the bottom of the social ladder were the laborers and slaves, who often worked the land and performed manual labor. This clear division of labor contributed to Sumer's economic success and cultural development.
Understanding the Sumer social structure allows us to appreciate the complexity of their society and the sophisticated systems that governed their interactions. The stratification not only dictated the social dynamics but also influenced the distribution of resources and wealth. In this article, we will explore the various classes within the Sumer social structure, the roles and responsibilities associated with each class, and the impact of this hierarchy on Sumerian society.
What Were the Main Classes in the Sumer Social Structure?
The Sumer social structure can be broadly categorized into four main classes: the ruling class, the priestly class, the commoners, and the slaves. Each class had distinct roles and responsibilities that contributed to the overall functioning of Sumerian society.
- Ruling Class: This elite group included kings, governors, and high officials who held significant power over political and military matters.
- Priestly Class: The priests were responsible for performing religious ceremonies and maintaining temples, acting as intermediaries between the gods and the people.
- Commoners: This group comprised farmers, artisans, and merchants who formed the backbone of the economy through their labor and trade.
- Slaves: Often captured during wars or born into servitude, slaves performed the most labor-intensive tasks and had few rights.
How Did Religion Influence the Sumer Social Structure?
Religion played a pivotal role in shaping the Sumer social structure. The Sumerians were polytheistic, worshipping numerous gods and goddesses who were believed to control various aspects of life. This belief system significantly impacted the social hierarchy.
The Role of Priests in Sumerian Society
Priests held a crucial position in the Sumer social structure, acting as powerful figures who interpreted the will of the gods. They were responsible for conducting rituals, maintaining temples, and ensuring that the community adhered to religious practices. Their influence extended beyond spirituality, as they often participated in political decision-making and economic planning.
What Were the Responsibilities of the Commoners?
Commoners formed the majority of the Sumerian population and were vital to the economy's functioning. Their primary responsibilities included:
- Agriculture: Farmers cultivated crops and raised livestock, providing food for the entire community.
- Artisanship: Skilled workers crafted tools, pottery, textiles, and other goods essential for daily life.
- Trade: Merchants facilitated commerce, exchanging goods with neighboring regions and contributing to economic growth.
How Did the Sumer Social Structure Evolve Over Time?
The Sumer social structure was not static; it evolved in response to various factors, including economic changes, warfare, and the rise of new city-states. As Sumerian society became more complex, the roles within each class became more defined, leading to a more organized social hierarchy. Additionally, the emergence of new political entities influenced the distribution of power and resources.
What Impact Did the Sumer Social Structure Have on Daily Life?
The Sumer social structure significantly impacted the daily lives of its citizens. Individuals' roles were largely determined by their social class, which dictated their access to resources, education, and political participation. For example, while members of the ruling class enjoyed privileges and wealth, commoners often faced challenges in securing basic necessities.
How Did the Sumer Social Structure Influence Future Civilizations?
The Sumer social structure laid the groundwork for future civilizations in Mesopotamia and beyond. Many aspects of Sumerian society, including the stratification of classes and the integration of religion and governance, were adopted and adapted by subsequent cultures. The legacy of Sumer continues to be felt today, as modern societies grapple with issues of social inequality and class divisions.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the Sumer Social Structure
In conclusion, the Sumer social structure played a vital role in shaping the dynamics of one of the world's earliest civilizations. Understanding this intricate hierarchy allows us to appreciate the complexities of Sumerian society and its contributions to human history. As we reflect on the Sumer social structure, we are reminded of the enduring impact of social organization on the development of cultures throughout time.
You Might Also Like
Discovering The Fascinating World Of Mammals That Lay EggsKeshia Knight Pulliam: A Journey Of Talent And Tenacity
Unraveling The Mystery Behind The Infamous 3 Guy 1 Hammer Video
Timothy Olyphant: A Multifaceted Talent In Hollywood
Understanding Patchy Eyebrows: Causes, Solutions, And Care Tips
Article Recommendations
- Greg Doucette Wife
- Deng Lun Wife
- Zach Callison Relationships
- Marcus Rosner Accident
- Does Harry Connick Jr Really Have Tattoos
- Jeffrey Nash
- Hunter Fieri
- Jacelyn Reeves
- Vegas 20 In
- Vegamovies Nl